- Gold spikes as investors seek safety after Trump’s day-one tariff threats.
- US Dollar Index drops, Treasury yields fall, both tailwinds for Bullion prices.
- Escalating Middle East tensions increases global uncertainty, boosting Gold’s safe-haven status.
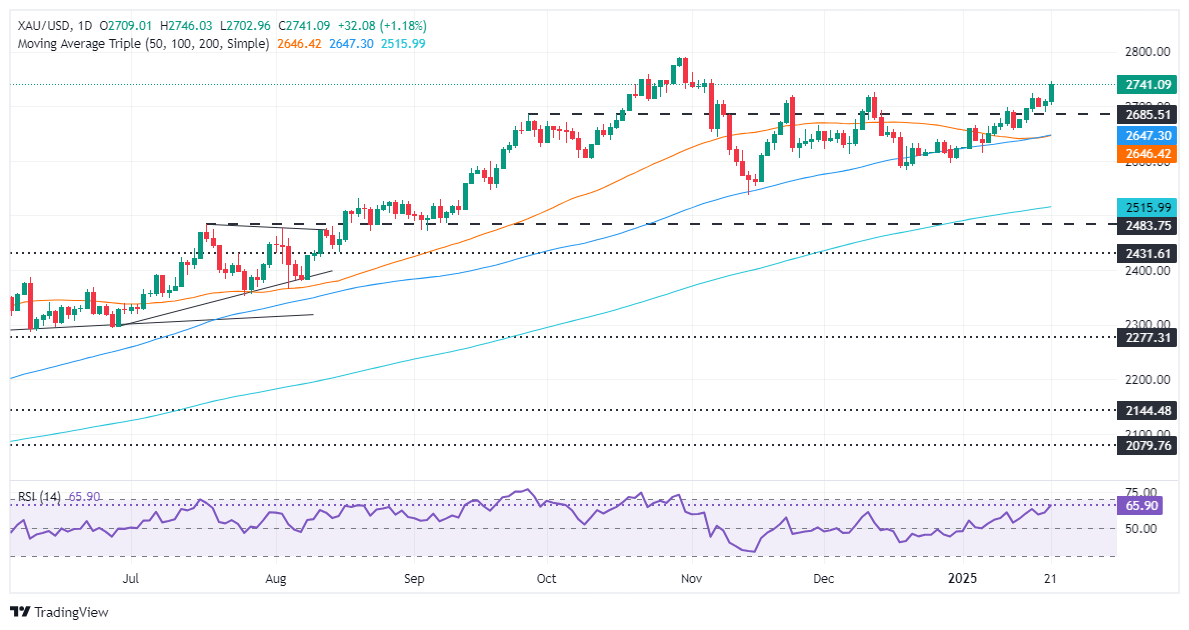
Gold rallied more than 1% and hit a two-month high of $2,745 on Tuesday as investors seeking safety bought the non-yielding metal following US President Donald Trump’s remarks on tariffs. The Greenback, which initially advanced, has turned negative as depicted by the US Dollar Index (DXY), a tailwind for Bullion prices. The XAU/USD trades at $2,742 at the time of writing.
Trump’s first day in office improved risk appetite, only to suddenly turn risk-averse after he hinted at imposing tariffs on Canada and Mexico as he signed a tranche of executive orders. The Canadian Dollar (CAD) and the Mexican Peso (MXN) tumbled, consequently sending the Greenback to a daily high of 108.79, according to the DXY.
Despite this, the precious metal continued to trend higher, clearing key resistance at $2,730. In addition, US Treasury bond yields are dropping in the belly and long end of the curve, bolstering Gold prices. The US 10-year T-note yield tumbled five-and-a-half basis points (bps) to 4.572%.
In the Middle East, the ceasefire agreement between Israel and Hamas was set aside as Israeli forces began an operation in the West Bank city of Jenin. In response, Hamas called for escalating the fighting against Israel.
This week, the US economic docket will feature Initial Jobless Claims data, S&P Global Flash PMIs, and housing data.
Daily digest market movers: Gold price soars as US yields retreat
- Gold price rises as real yields tumbled three basis points. Measured by the 10-year Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) yield sits at 2.17%.
- President Trump confirmed that universal tariffs on all imports to the US are under consideration as well and will come at a later stage, Reuters reports.
- Market participants are pricing in near-even odds that the Fed will cut rates twice by the end of 2025, with the first reduction occurring in June.
XAU/USD technical outlook: Gold price breaks higher toward $2,750
The uptrend in Gold prices resumed after bulls had failed to clear the December 12 daily peak of $2,725. This opened the door for challenging the psychological $2,750 figure, and the record high at $2,790 ahead of $2,800.
Conversely, if sellers drive XAU/USD below $2,700, the first support would be the January 13 swing low of $2,656, followed by the confluence of the 50 and 100-day Simple Moving Averages (SMAs) at $2,642 to $2,644.
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.