Materials and reagents
Fresh Indocalamu Iatifolius McClur leaves were acquired randomly from an online store and a supermarket that specializes in selling Indocalamu Iatifolius McClur leaves. These leaves were authenticated as fresh leaves from the Indocalamus Iatifolius (Keng) McClure, a species of broad-leaved bamboo, by Professor Wang Xiangpei from Guizhou Minzu University. Kunming mice, 18–22 g of body weight, and half of male and female, were procured from Chongqing Tengxin Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Several chemicals were employed in the study, including nitric acid (purity > 99.8%), hydrogen peroxide (purity > 99.8%), and hydrochloric acid (purity > 99.8%), ascorbic acid (purity > 99.7%), potassium borohydride (purity > 99.8%), sodium hydroxide (purity > 99.8%), copper (GSB 04-1725-2004, 1000 µg/mL), lead (GSB 04-1742-2004, 1000 µg/mL), cadmium (GSB 04-1721-2004, 1000 µg/mL), mercury (GSB 04-1729-2004, 1000 µg/mL), and arsenic (GSB 04-1714-2004, 1000 µg/mL) were also utilized. The medium employed was 1.0 mol/L HNO3 sourced from the National Nonferrous Metals and Electronic Materials Analysis Testing Center. Other materials included nitrogen gas (purity > 99.99%), etc.
Methods
Acute toxicity experiment of Indocalamu Iatifolius McClur leaves
The two types of Indocalamu Iatifolius McClur leaves were individually weighed and boiled in ten times the amount of water for 30 min. This extraction process was repeated three times, and the filtrates were combined and subsequently filtered. The resulting solution was concentrated to form a suspension that could pass through a No.12 gastric tube. Based on calculations, the concentration of the aqueous Indocalamu Iatifolius McClur leaves extract was determined to be 2 g (crude drug) per mL.
All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. Animal experiments were performed in accordance with ARRIVE guidelines. Protocols were approved by the experimental animal ethics committee of Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (ethics reference number: 20230030). A total of 60 healthy Kunming mice, with a weight range of 24–30 g and an equal distribution of males and females, were chosen for the study. They were housed under controlled conditions, with an ambient temperature of 22 ± 2 °C, a humidity level of 60 ± 5%, and a 12-h light/dark cycle. Prior to the experiments, the mice underwent a 7-day acclimation period under these conditions. Subsequently, the mice were randomized into a blank control group, a Indocalamu Iatifolius McClur leaves (online store) group, and a Indocalamu Iatifolius McClur leaves (supermarket) group. Prior to drug administration via gastric gavage, the mice fasted for 12 h. The administration volume was 0.4 mL per 10 g of body weight. Mice in the blank control group received physiological saline via gastric gavage, while the other groups were given the corresponding Indocalamu Iatifolius McClur leaves extracts. The maximum dose was administered within 24 h, with two administrations occurring within this timeframe. Following administration, the mice were continuously monitored for signs of toxicity or mortality, and their general condition and body weight changes were recorded for 14 days. The mice used for experiments were euthanized using cervical dislocation after the use.
Biochemical analysis of mouse blood parameters
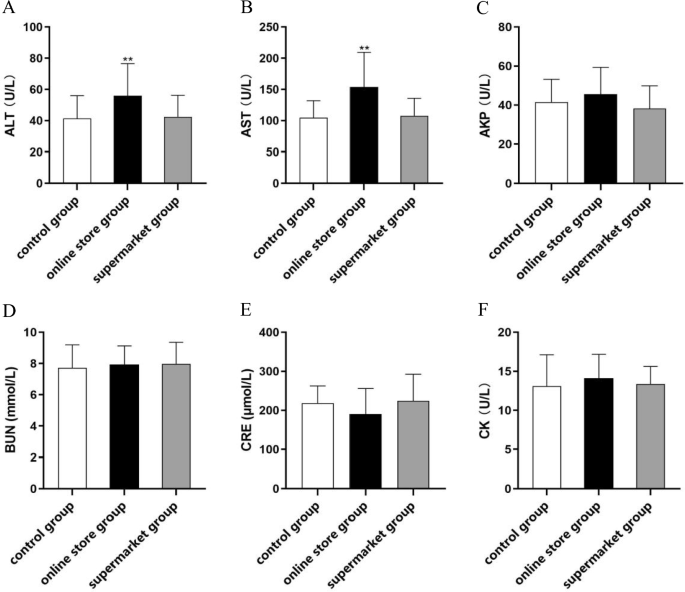
After a 14-day administration period, the eyeballs of mice from each group were dissected to collect blood samples. These samples were then centrifuged to obtain the serum. Biochemical indicators associated with liver function, including alkaline phosphatase (AKP), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT), were measured using a biochemistry analyzer. Similarly, indicators related to kidney function, such as blood creatinine (CRE) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN), were measured. Furthermore, the cardiac function indicator, creatine kinase (CK), was examined.
Pathological observations of mouse heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney tissues
In animal mortality, deceased mice were promptly dissected to assess potential pathological alterations in the heart, liver, spleen, lungs, and kidneys. After 14 days, the remaining mice were euthanized following blood collection and removal of their eyeballs. Thorough macroscopic observations were documented concerning pathological changes in the liver, lungs, heart, spleen, and kidneys. Subsequently, tissue samples were fixed in a 4% paraformaldehyde solution, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (HE), and examined for histopathological modifications.
Determination of copper, lead, and cadmium contents in Indocalamu Iatifolius McClur leaves by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES)
The determination method for copper, lead, and cadmium content, in accordance with the National Food Safety Standard, was employed18. A precise weight of approximately 0.2 g of finely ground sample was placed in a digestion tank, followed by the addition of 5 mL of nitric acid. The mixture was thoroughly shaken and allowed to stand overnight. Subsequently, the sample was decomposed at a low temperature, and 2 mL of nitric acid and hydrogen peroxide were added and mixed for microwave digestion. Once digestion was completed and the solution was cooled, the excess acid was evaporated in the graphite furnace until approximately 1 mL remained. The solution was then diluted to a final volume of 25 mL in a volumetric flask. Before analysis, the ICP was preheated for more than 4 h and ventilated for over 1 h. Following stabilization, the levels of lead, cadmium, and copper were measured. The parameters for the ICP-OES instrument were set as follows: an excitation power of 1.1 KW, cooling gas flow rate of 18.0 LPM, nebulizer gas pressure of 34.0 PSI, auxiliary gas flow rate of 0.0 LPM, optical chamber purge gas flow rate of 0.77 LPM, detector temperature of 40 °C, thermostat inlet temperature of 35.0 °C, horizontal time of 1 s, vertical time of 10.00 s, and an injection volume of 1.4 mL/minute.
Determination of mercury and arsenic contents in Indocalamu Iatifolius McClur leaves by atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS)
The determination method for mercury and arsenic content, in accordance with the National Food Safety Standard, was utilized18. Approximately 0.2 g of finely ground sample was accurately weighed and placed in a digestion tank. Then, 5 mL of nitric acid was added, and the mixture was thoroughly shaken and left to stand overnight. Following this, the sample was decomposed at a low temperature, and 2 mL of nitric acid and hydrogen peroxide were added and well-mixed for microwave digestion. Next, 5 mL of the digestion solution was transferred into a 10 mL colorimetric tube, and 1 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid and 1 mL of 5% (thiourea + ascorbic acid) were added. The mixture was then made up to a final volume of 10 mL with ultrapure water. After shaking for 30 min, the levels of mercury and arsenic in the solution were measured using an atomic fluorescence spectrophotometer. The carrier gas used was 5% hydrochloric acid, and the reducing agent consisted of a 2% potassium borohydride and 0.5% sodium hydroxide solution. The instrumental parameters for the AFS instrument were as follows: a working lamp Se lamp, negative high voltage of 300 V, total lamp current of 50 mA, lamp current of 25 mA, carrier gas flow rate of 300 mL/min, shield gas flow rate of 800 mL/min, and atomizer height of 8 mm.
Determination of nine organochlorine pesticide residues in Indocalamu Iatifolius McClur leaves by gas chromatography (GC)
The sample preparation method for determining nine residues of organochlorine pesticides followed the first method outlined in the Fourth Part of the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia19. Chromatographic conditions for sample detection were as follows: a capillary column consisting of 86% dimethyl polysiloxane and 14% methyl polysiloxane (cyanopropylphenyl) with an inner diameter of 0.32 mm, a length of 30 m, and a film thickness of 0.25 µm was employed as the stationary phase. The inlet temperature was set at 230 °C, and the detector temperature was maintained at 300 °C without split injection. The temperature program for analysis involved an initial temperature of 100 °C, followed by an increase of 10 °C /min until reaching 220 °C, then an increase of 8 °C /min until reaching 250 °C, which was held for 10 min.
Data analysis
The data are summarized as mean ± standard deviation. Statistical analysis was conducted utilizing SPSS 27.0 software. A T-test was utilized for comparisons between two groups, whereas one-way ANOVA was employed for comparisons among more than two groups. Significance was indicated by P < 0.05 or P < 0.01.
Plant guideline statement
Experimental research and field studies on plants (either cultivated or wild), including the collection of plant material, must comply with relevant institutional, national, and international guidelines and legislation. We adhere to the IUCN Policy Statement on Research Involving Species at Risk of Extinction and the Convention on the Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora.